Manholes: The Ultimate Resource
Covers, accessories, engineering, installation, maintenance and more. Everything you’ve ever wanted to know about the underground world of manholes.
What is a Manhole?
According to Dictionary of Construction, a manhole is, “a vertical access shaft from the ground surface to a sewer or stormwater line…, usually at a junction, to allow cleaning, inspection, connections, and repairs.”

What is the Purpose of a Manhole?
As manhole manufacturers, we often get asked about the purpose of manholes and the uses of manholes. And the answer is, that there are many functions of manholes when it comes to sewer or stormwater systems. The four main purposes of a manhole are:
- To facilitate inspections of the sewer or stormwater system as well as maintenance projects such as cleaning or removal of obstructions within the sewer or stormwater line
- To assist in ventilation of the sewage system by allowing gases to escape
- To allow the municipality to join sewer or stormwater systems, change the direction of the sewer or stormwater system, or align the sewer or stormwater system
- To assist in ensuring the sewer or stormwater line is laid in convenient lengths


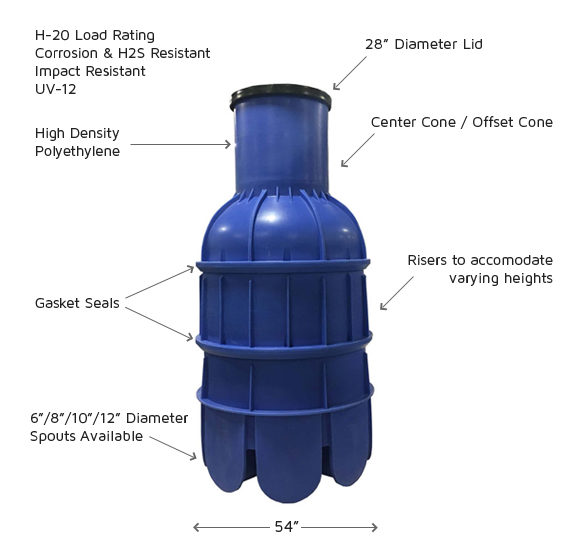
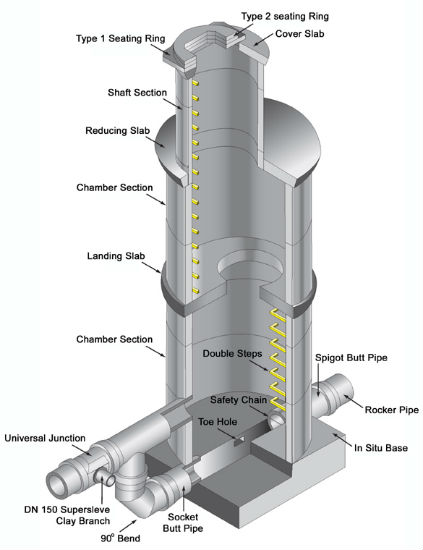
 Due to the engineering and maintenance issues associated with cast iron manholes, a variety of alternative manhole cover types have increased in popularity in recent years including composite materials, plastics, and fiberglass. Some of the major benefits [
Due to the engineering and maintenance issues associated with cast iron manholes, a variety of alternative manhole cover types have increased in popularity in recent years including composite materials, plastics, and fiberglass. Some of the major benefits [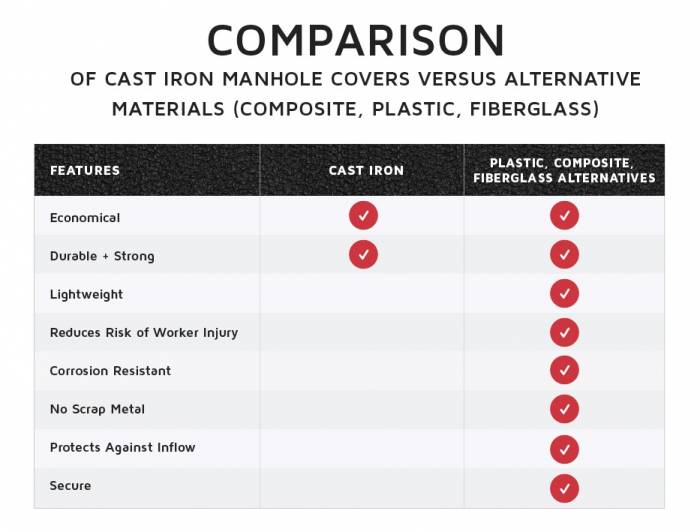
 In order to keep your city’s sewer or stormwater system functioning properly, and in order to maintain public safety, regular maintenance on manholes is critical. Common manhole maintenance tasks [
In order to keep your city’s sewer or stormwater system functioning properly, and in order to maintain public safety, regular maintenance on manholes is critical. Common manhole maintenance tasks [







